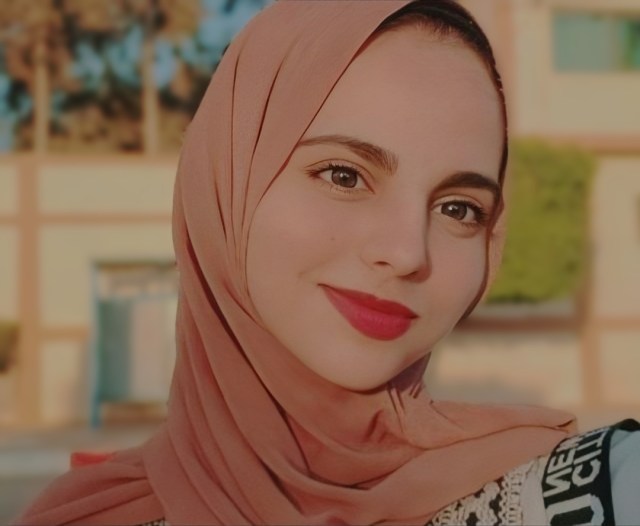
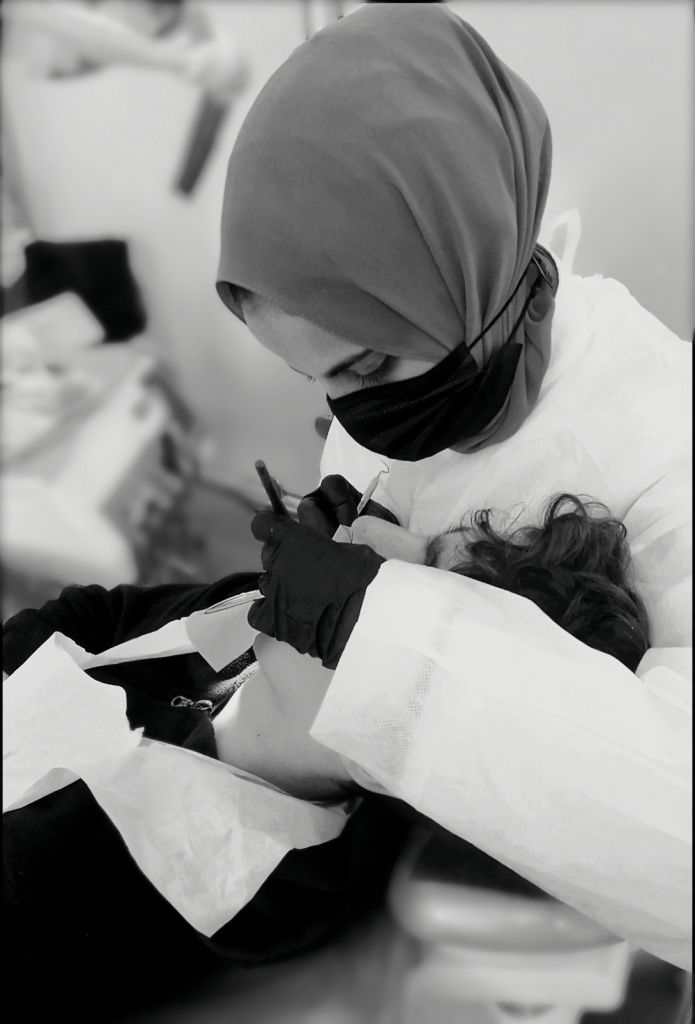
Dina Turkeya is a Palestinian dentist, author and translator. Her family is originally from Yaffa, but she was born and raised in Gaza. She has survived eight wars and aggressions, and still holds onto her dreams and ambitions. Dina’s love for her homeland inspired her to write her debut book, Time To Know Palestine (2024). She is interested in learning languages, writing, drawing and exploring different cultures.
Gaele Sobott: Please tell us a little about your family, including where they originate from and how their experiences have impacted your life.
Dina Turkeya: My great-grandfather was Turkish. He moved to Palestine in the early 1900s and married in Yaffa, where my grandfather was born. After the Nakba of 1948, my grandfather and his family were forcefully displaced to Gaza. He left everything they owned to start from scratch with the label ‘refugees’ on their identification cards. I still remember how my grandfather longed to return to Yaffa, their lovely house and the orange groves. He was waiting for the moment when his feet would touch his homeland after years of deprivation, but what happened was another Nakba. He was displaced from his house in Gaza to a tent in the south of Gaza in this ongoing war. His body couldn’t bear the inhuman conditions and the heartbreak of displacement again, and he died in the tent after years of suffering and yearning.
GS: Where/when were you born? Describe that place and tell us about your time growing up, including your experiences with siblings, cousins and school friends.
DT: I was born in December 2001 and lived my whole life in a very beautiful city called Al-Zahra. This coastal city is nestled in the heart of the Gaza Strip, boasting stunning natural beauty with lush trees, vibrant flowers, serene and spacious streets and kind locals. Growing up, I resided in our lovely house for about 22 years, which witnessed my earliest steps, first words, school journey and university studying nights. Every laugh, tear and whoop echoed through its walls. It was everything to me.
I had plenty of friends there and neighbours like a second family. I am the eldest of three siblings. We’d grown up in a family atmosphere full of love, involvement and support. My cousins were more than relatives. We gathered every Thursday, talked and shared our updates and stories, played cards and challenge games, ate delicious homemade food and desserts, watched movies and celebrated our special days. These weekly gatherings were cherished moments of respite from our bustling lives. I was fortunate to have wonderful friends I met through school, volunteer work, training programmes and even online international courses. True friends simplify life by offering guidance and support, celebrating victories and lightening the load on tough days.
GS: Apart from Arabic, what other languages do you speak? Where/how did you learn these languages?
DT: I speak English, Spanish and French. I’ve always been passionate about learning new languages. For me, language is not only a tool for communication but also a gateway to discover the world, learn new insights and open doors for new opportunities. My English proficiency was honed through school education and active participation in English clubs and programs. Similarly, I studied French for three years in primary school and continued for two years in secondary school, culminating in taking the DELF exam. Additionally, I dedicated three years to learning Spanish at Instituto Cervantes during my university years.
GS: Tell us what roles different languages play in your life and how different languages give or subtract from your view of the world.
DT: Arabic is my mother tongue; a rich, sophisticated and poetic language. The musicality and rhythm of Arabic, along with its diverse dialects adds to its charm and beauty. While I have studied many languages, none possess the deep meanings and elegant words found in Arabic.
Mastering languages has opened numerous opportunities for me, enhancing my skills in both personal and professional aspects. It helped me understand other cultures and perspectives, especially since living in Gaza has restricted my ability to travel and explore the world freely. Travelling is not a luxury when you reside in Gaza. It involves encountering various challenges along the way.
GS: Describe how the Zionist occupation of Palestine impacted your life from a young age. If it is not too much for you, can you comment on your experiences of the current genocide in Gaza?
DT: Throughout my 22 years in Gaza, I endured eight wars and aggressions, which left me grappling with feelings of instability and the lasting effects of violence and trauma. The constraints of the siege limiting our freedom of movement, the scarcity of electricity, and the obstacles to accessing education, healthcare, and economic opportunities all contributed to a persistent sense of hardship.
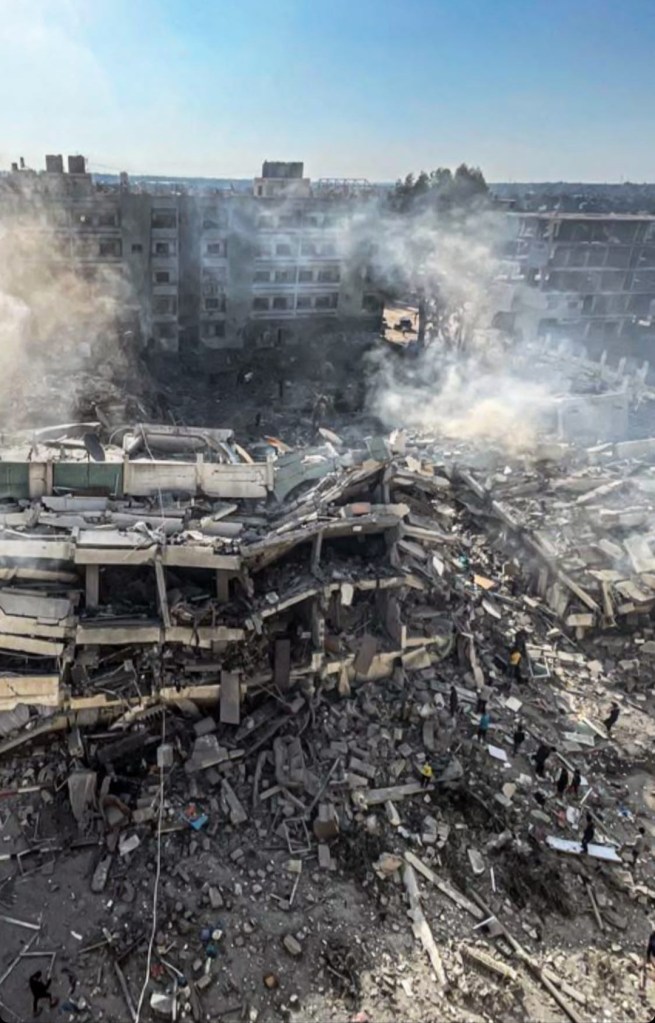
I still remember every detail of that unforgettable day on the 19th of October 2023, around 6:30 in the morning. A man’s loud cry of “Get out of your homes” jolted me awake in a panic, prompting me to rouse my family. We hastily left with only essential documents and some money. Seeking refuge at our aunt’s house down the street, we were startled by a deafening explosion, followed by another. The smoke was suffocating, my heart was about to stop from the intensity of the explosion. The shock and horror of losing our home hit hard as we realised it was our building that had been destroyed. I lost the place where I felt safe, warm, grateful and happy. I lost my sweet memories. I’m the kind of person who likes to save everything. I saved my childhood photos, the old coins, gifts and letters from my friends and family, my summaries, drawings and pieces of writing. I lost everything in the blink of an eye.
During the night, when the city was enveloped in darkness, we were startled by the sound of people running and screaming in the streets. We were informed that Israel was planning to bomb more than 25 towers in Al-Zahra city. Confused and frightened, we rushed out into the streets, unsure of where to go. Moments later, as the bombings commenced, the deafening explosion knocked us to the ground, prompting us to flee as far as we could.
More than 16,000 people found themselves on the streets. Surrounded by fire, the towers were under attack from the south, while nearby cities were being bombarded from the north. War boats approached from the west and tanks advanced from the east. Amidst this turmoil, babies were crying, the elderly were sitting in wheelchairs, women were screaming in terror and men attempted to calm down their families. I remember that even the dogs were running in panic at the sound of explosions, seeking refuge among the people. What happened is beyond the endurance of any human being and any creature with a heart and mind.
We spent 15 hours in horror; we were afraid, exhausted, cold, hungry and heartbroken. Not only the residents of Al-Zahra city witnessed this difficult night, but also other displaced people who had sought shelter in Al-Zahra after fleeing their houses. It was the hardest night of my life. I didn’t think that we would be alive the next day. I remember waiting for the sun to rise to warm us with its rays. The devastated city was shrouded in grey smoke, evoking a sombre atmosphere. We eventually evacuated to the south of Gaza, and tears welled in our eyes. Witnessing my once-vibrant neighbourhood reduced to rubble was heart-wrenching; a place that had once bloomed with flowers and love.
Even worse, Al Zahra city has lost all its landmarks and has been completely devastated by the continued bombing. Our city was built in 1998 to stop the expansion of Israel’s Netzarim settlement situated to the North. Netzarim was the last settlement to be evacuated and demolished by Israel when they withdrew from the Gaza Strip in 2005. Now, history repeats itself in an even more dreadful form. After forcibly displacing all the people in the area during the first weeks of this war of genocide, Israel created the Netzeim Corridor to divide the Gaza Strip into northern and southern zones. They did this by destroying everything in their way, including our beautiful city.
The bombs killed my cousin in cold blood. She was staying with her husband’s family. I didn’t get the chance to say goodbye to her before I left. She was dead under the rubble. It is heartbreaking not to be able to visit her grave, lay flowers or properly mourn her death. The harsh reality of her non-existence brings to mind the concept of annihilation. The pain is profound when someone you shared precious moments with — chatting, laughing, watching sunsets — is gone forever, and we have even been deprived of the solace of burial and mourning rituals.
Many of my friends and colleagues were killed as well. Each of them had dreams and worked hard to create a brighter future. They were simply trying to live, yet what they received was death. It is extremely hard for me to look at their pictures and realise that I will never see them again or hear their voices. I find myself recalling every conversation and every moment spent together. However, what brings me solace is the thought that they are in a better place, away from this evil and brutality. Their souls deserve peace and purification from this harsh world.
GS: Please talk about your tertiary education. What did you choose to study and why? Where did/do you study?
DT: I was studying dentistry at the University of Palestine. I have chosen this speciality because I feel that relieving a patient’s pain and giving him/her the confidence to smile is out of this world. I was in my final year when the war happened. I was so excited for my graduation after five years of hard work. It was the moment to reap the fruits of my efforts. I had many plans and dreams, envisioning everything as if painting a beautiful picture. War disrupted my plans, leaving me unable to complete my studies due to the destruction of my university. This unexpected turn of events forced me to put my dreams on hold, leaving me with a sense of loss and uncertainty. It’s truly heartbreaking to see how drastically our lives have changed, knowing that things will never be the same again.
GS: Tell us about your experience of leaving Gaza.
DT: Leaving Gaza was the hardest decision we have ever taken. My parents decided to save the last thing that was left, which was “us”. We left in late January 2024 after four months of hardship and witnessing brutal atrocities. Leaving isn’t an option available to everyone. It’s costly and takes a long time. I left behind my beloved family, relatives, friends and neighbours. It felt like my soul had been taken from my body when I received the news that we were leaving. The farewell and our last hugs were so painful, with uncertainty looming over us of whether we would ever see each other again, knowing everyone was at risk of being killed at any moment. The first steps outside Gaza made me feel traumatic shock. A sky without the sound of drones, lights in the streets at night, the feeling of safety where we were staying, knowing that the building wouldn’t be bombed over our heads, charging our phone anytime, having good internet, drinking clean water and food, sleeping in a bed, washing our clothes in the washing machine not manually. These small details have been transformed into distant dreams for every Gazan.
The first months were so hard. My mind couldn’t comprehend what had happened to us, how much the profound loss weighed heavily on our hearts, and how it would be possible for us to live with such emptiness in our souls. It hurts so badly to live with those reoccurring flashbacks of our old life, stuck in the past but hoping that something will happen to bring life and hope to us again. Hearing and reading the news is much more painful, especially since we can’t reach people in Gaza due to the deliberate destruction of the internet and telephone network. We are continually anxious, waiting for a response and fearing that we will see the names of our loved ones on the list of martyrs.
All the people who survived the war share the same pain; we all tell similar stories of our suffering. Wounded people bandage each other’s wounds! I thought that after moving abroad, I could continue pursuing my dreams, only to encounter a harsh reality of exploitation and obstacles placed in our path instead of understanding our circumstances.
GS: You are about to publish your book, Time To Know Palestine. Tell us what this book is about and why you wrote it.
DT: After surviving the war in Gaza, I was trying to recover from the trauma and writing was my way of healing. It was so difficult to turn all the indescribable emotions into words. I was initially unable to concentrate or communicate properly. My family encouraged me to start writing, and I am very grateful to my friend Ana for her unwavering support. She connected me to incredible people from Palestine (West Bank and 48 Lands). They answered all my inquiries and showed me pictures and videos of the places that brought tears to my eyes. It’s so unfair when you can’t visit your homeland while everyone else, including the occupiers, can freely explore its beauty, stroll along its streets and visit all its attractions.
Time To Know Palestine is my way of showing love, pride and respect for Palestine and Palestinians. It’s a message to humanity to see the beauty of my country and know about its long-standing history and vibrant culture. It acknowledges each voice that has been silenced.
This book is for all the lucky people who had or will have the opportunity to live the most beautiful days and memories of their lives in Palestine. And for every Palestinian who is deprived of seeing the beauty of his homeland because of the occupier’s unjust policies.
I will take you on a journey through my words, which I wrote with love and sincerity so that you receive the complete true picture of Palestine, despite all the desperate attempts of the occupier to Judaize and erase its history and geography. This book represents the voice of Palestine that will echo through the centuries, the voice of truth and the voice of the awaited freedom. — Time To Know Palestine
GS: What types of international support for Palestine would you like to see happening at this point?
DT: People worldwide have shown great solidarity for Palestine and its people, starting from the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) movement, which proved its effectiveness. Activism and solidarity campaigns to raise international awareness about the Palestinian issue, the human rights abuses in the occupied Palestinian territories and the victims of the genocide. Grassroots campaigns and protests to support the Palestinian people’s struggle for freedom, justice and equality are growing.
I believe that civil society and social movements play a crucial role in influencing decision-making by applying pressure on governments to implement policies that address the needs and aspirations of everyday people. Many think that providing humanitarian aid and donations to Palestine suffices. However, the real solution lies in tackling the root causes of this ongoing suffering: ending the occupation and halting the genocides.
GS: As one of the places this interview will be published is a zine that will be circulated among young people who like electronic music, I am wondering what types of music you like? What are two of your favourite songs right now?
DT: I like classical music because of its ability to evoke deep emotions and transport me to another world. There is something incredibly calming about the sound of the piano, it helps me unwind and clear my mind. My musical preferences vary depending on my mood and what I’ve been going through recently. Right now, my favourite songs are “I’m Coming Home” by Skylar Grey, and “Gonna Be Okay” by Brent Morgan. They describe the nostalgia I feel for my homeland, my efforts to overcome difficult times and the pursuit of hope.
GS: What are you currently reading?
DT: Most of what I read currently is about dentistry to ensure I don’t forget the knowledge I’ve gained over the past few years and stay updated with new advancements.
GS: What message would you like to send to your generation internationally?
DT: To my generation internationally, I would say: we hold the power to create a more just, compassionate and peaceful world, but it demands collective action, empathy and a genuine willingness to listen and understand each other. In this era of global connectivity, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the obstacles we face, but we must remember that we are also better equipped than ever to make a meaningful impact.
We must advocate for human rights, justice, and equality, recognising that the struggles of one community affect us all. Let’s leverage our platforms, education and resources, not only to improve our own lives but also to stand in solidarity with those enduring oppression and hardship. Let’s actively seek diverse perspectives, build connections, and act with empathy and courage.
Our generation has the potential to transform the narrative — from division to unity and from indifference to proactive compassion. The future hinges on how we engage with the world today and each of us plays a vital role in making it brighter.
GS: Describe what you most admire about Palestine.
DT: At this point in history, what I find most admirable about Palestine is the resilience of its people. Despite enduring decades of hardship, displacement and conflict, Palestinians continue to exhibit remarkable strength and determination. Our capacity to preserve our culture, traditions and sense of identity in the face of adversity is genuinely inspiring.
I am also impressed by the younger generations in Palestine who are actively embracing education, technology and activism to amplify their voices on a global platform. We demonstrate creativity, resourcefulness and a passionate commitment to shaping a brighter future, often employing art, literature, and social media to convey our hopes and challenges.
Furthermore, I have great respect for how Palestinian communities worldwide have managed to maintain their identity, fostering a strong sense of solidarity and pride in our shared heritage, even while in the diaspora. The enduring spirit of perseverance and the continual hope for justice and freedom serve as a powerful testament to the strength of the Palestinian people.
GS: What future do you envisage for Palestine?
DT: The future I wish for Palestine is one where its people enjoy freedom and independence, liberated from the oppression of occupation, living in a secure and culturally and economically prosperous state. I wish for Palestine to reclaim its status as a beacon of knowledge, creativity and peace, just as it was before the onset of occupation.
This interview was conducted in English with Dina Turkeya by Gaele Sobott in September 2024.
Purchase a Copy of Time To Know Palestine
Connect with Dina Turkeya on LinkedIn
Gaele Sobott writing, culture, social & economic justice by Gaele Sobott is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International